Table of Contents
Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Security Certifications: Boost Your Cybersecurity Career
In the modern era of ubiquitous connectivity, where the digital fabric of organizations is under constant siege, the risks posed by cyber threats have escalated to unprecedented levels. Data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other forms of cyber exploitation not only jeopardize operational integrity but also expose organizations to severe reputational and financial repercussions. To counteract these pervasive risks, vulnerability assessment emerges as an indispensable pillar of cybersecurity resilience, working synergistically with other measures such as incident response planning, threat intelligence integration, and continuous monitoring to create a holistic defense strategy. This discourse aims to elucidate the multifaceted dimensions of vulnerability assessment, providing a scholarly exploration for fortifying organizational defenses.
The dynamic and evolving nature of cyber threats necessitates a vigilant and adaptive approach. Contemporary cyber adversaries exhibit remarkable ingenuity, often deploying sophisticated automated tools to uncover latent vulnerabilities within IT ecosystems. Consequently, the institutional adoption of a systematic framework to identify, evaluate, and prioritize these vulnerabilities transcends operational preference and becomes an imperative. Such a framework encompasses key elements, including robust vulnerability scanning tools, integration with threat intelligence feeds, and a clear prioritization methodology based on asset criticality and exploitability. By combining automated solutions with expert analysis, organizations can ensure that the framework remains adaptable to emerging threats and aligned with overarching cybersecurity objectives. Neglecting this proactive methodology renders organizations susceptible to data compromise, erosion of stakeholder confidence, and non-compliance with stringent regulatory frameworks—outcomes that may prove existentially detrimental.
What is Vulnerability Assessment?

A vulnerability assessment is a structured process to identify, evaluate, and prioritize weaknesses in an organization’s IT infrastructure, including networks, applications, and systems. It is a cornerstone of any robust cybersecurity strategy, enabling businesses to address potential threats before they lead to significant damage.
In addition to identifying weaknesses, vulnerability assessments help organizations stay updated with the latest threats and security standards. As attackers employ advanced methods, periodic assessments ensure that businesses do not lag in their defenses. Moreover, vulnerability assessments provide crucial data for decision-making, enabling IT teams to allocate resources effectively.
Why is Vulnerability Assessment Important?

Proactive Threat Management
Vulnerability assessments allow organizations to pinpoint and address vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them, ensuring a proactive security posture.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries must adhere to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) governs data protection and privacy in the European Union, HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) sets standards for protecting sensitive health information in the United States, and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) establishes security measures for organizations handling credit card data. These regulations mandate stringent safeguards, periodic assessments, and reporting to ensure compliance and mitigate security risks. Regular assessments help meet compliance requirements, avoiding hefty fines and reputational damage.
Regulatory bodies frequently update their guidelines to address emerging threats. Conducting regular assessments ensures that businesses remain compliant and prepared to pass security audits, which can be critical in highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare.
Enhanced Risk Management
Understanding the severity and potential impact of vulnerabilities enables businesses to prioritize remediation efforts, focusing resources where they are needed most.
Risk management is not just about fixing vulnerabilities; it’s also about understanding their broader implications. For instance, a vulnerability in a database containing sensitive customer information might warrant a higher priority than one in a less critical system.
Maintaining Customer Trust
By safeguarding sensitive data, businesses build and maintain trust with customers and stakeholders, a critical factor in today’s competitive market.
In an age where data breaches make headlines regularly, customers expect organizations to take cybersecurity seriously. A well-implemented vulnerability assessment process demonstrates a commitment to protecting customer data and fosters long-term loyalty.
Key Steps in the Vulnerability Assessment Process
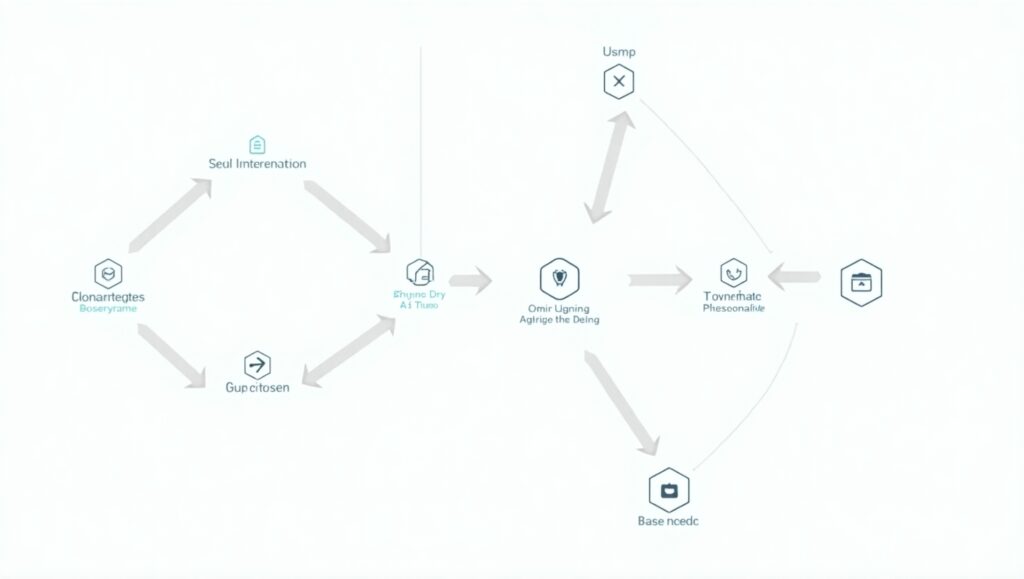
Planning and Scoping
This initial phase lays the groundwork for the assessment by defining its scope, including the assets, networks, and applications to be analyzed. Key stakeholders are identified, and clear objectives are set to align the assessment with organizational goals. Regulatory requirements or industry-specific threats are also considered to ensure relevance.
Scanning and Identification
Using automated tools, systems are scanned for known vulnerabilities. These tools reference extensive vulnerability databases to identify weaknesses such as unpatched software, misconfigurations, or outdated systems. Comprehensive scanning must encompass all layers of the IT environment, including often-overlooked elements like cloud infrastructure.
Classification and Analysis
Identified vulnerabilities are prioritized based on severity, potential impact, and exploitability. An evaluation of how these vulnerabilities could disrupt critical business operations is conducted. Threat intelligence is leveraged to provide context and assess the relevance of each vulnerability to the organization’s unique risk landscape.
Remediation
This step involves implementing fixes, such as applying patches, reconfiguring systems, or upgrading outdated hardware and software. Action plans are developed for vulnerabilities that require long-term solutions. Follow-up testing validates remediation efforts, ensuring vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed.
Reassessment and Reporting
Post-remediation, a reassessment ensures that the fixes are successful and no residual vulnerabilities remain. Detailed documentation of findings, actions taken, and future recommendations is provided to stakeholders, fostering transparency and continuous improvement.
A successful vulnerability assessment involves the following steps:
Planning and Scoping
- Define the assessment’s scope, including the assets, networks, and applications to be analyzed.
- Identify key stakeholders and set clear objectives for the assessment.
- Consider regulatory requirements or specific threats relevant to your industry.
Scanning and Identification
- Use automated tools to scan systems for known vulnerabilities, referencing extensive vulnerability databases.
- Identify weaknesses such as unpatched software, misconfigurations, or outdated systems.
- Ensure that scanning covers all layers of the IT environment, including cloud infrastructure, which is often overlooked.
Classification and Analysis
- Prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity, potential impact, and exploitability.
- Evaluate how vulnerabilities could affect critical business operations.
- Leverage threat intelligence to contextualize vulnerabilities and assess their relevance to your organization.
Remediation
- Implement fixes such as applying patches, reconfiguring systems, or upgrading outdated hardware or software.
- Develop action plans for vulnerabilities requiring long-term mitigation.
- Ensure that remediation efforts are validated through follow-up testing to confirm that vulnerabilities have been resolved.
Reassessment and Reporting
- Verify that vulnerabilities have been resolved by performing follow-up assessments.
- Document findings and actions taken to maintain a transparent record of cybersecurity efforts.
- Use reports to inform stakeholders about progress, challenges, and areas requiring additional focus.
Types of Vulnerability Assessments
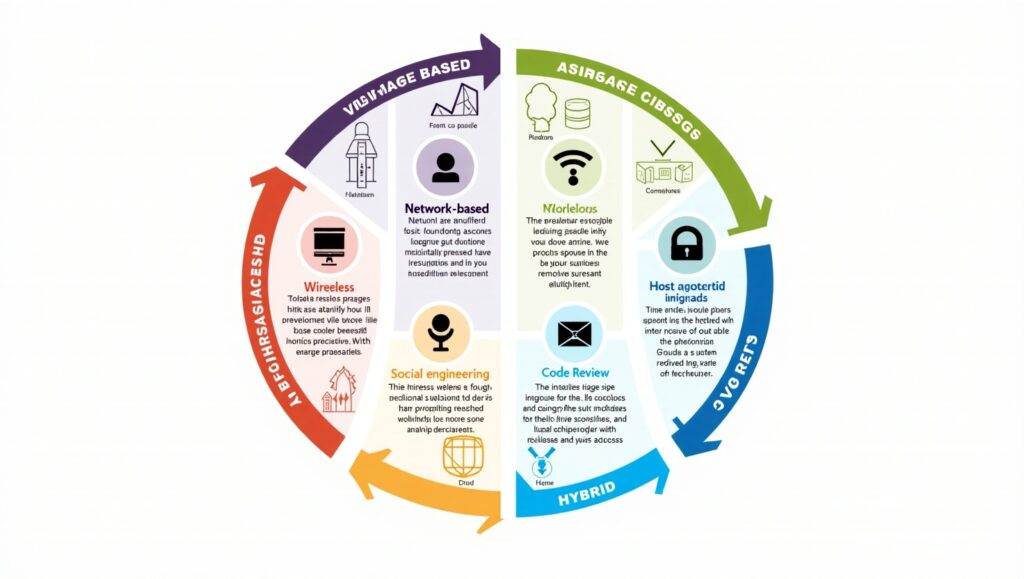
Vulnerability assessments can target various aspects of an organization’s IT ecosystem. Below are the primary types:
Network-Based Assessments
- Focus on identifying vulnerabilities in routers, switches, firewalls, and other network devices.
- Evaluate the overall security of network architecture.
- Assess network segmentation to ensure that sensitive data is adequately isolated.
Host-Based Assessments
- Assess individual devices, including servers and workstations, for misconfigurations, open ports, and vulnerabilities in running services.
- Ensure that critical endpoints are included in the scope, especially those used for remote work.
Application-Based Assessments
- Analyze web and mobile applications for security flaws such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), or insecure authentication mechanisms.
- Incorporate testing for APIs, which are increasingly targeted by attackers.
Database Assessments
- Identify weaknesses in database configurations, encryption protocols, and access controls to prevent unauthorized data access.
- Ensure that backup systems are secure and included in the assessment.
Tools for Conducting Vulnerability Assessments
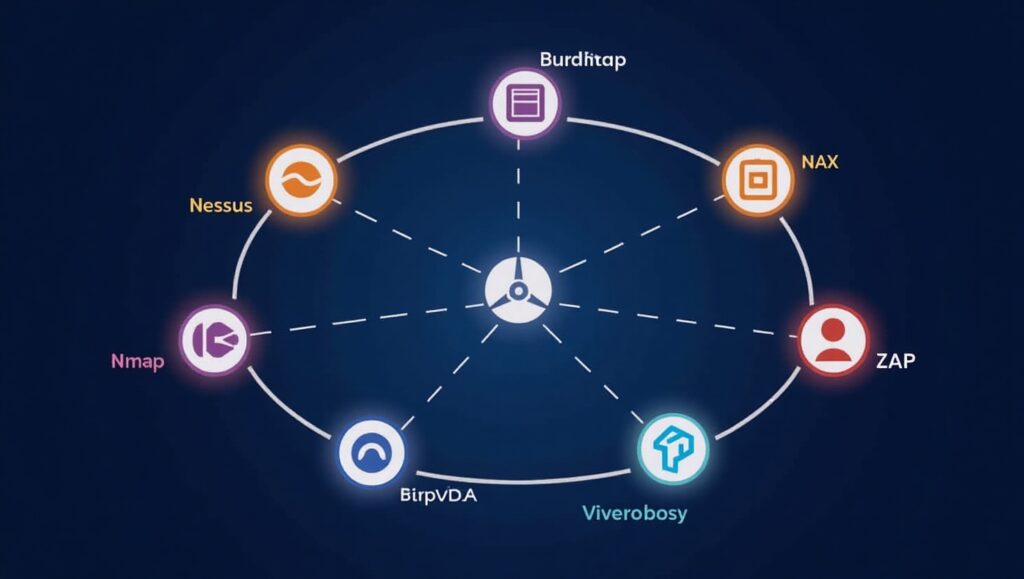
Organizations rely on various tools to streamline vulnerability assessments, including:
- Nessus: A popular tool for comprehensive network and system scans.
- OpenVAS: An open-source solution for detecting and managing vulnerabilities.
- Burp Suite: Widely used for testing application security.
- Qualys: Offers cloud-based vulnerability scanning and management.
- OWASP ZAP: A free tool focused on web application security.
In addition to these tools, many organizations employ specialized software for monitoring and alerting, which works in tandem with vulnerability assessments to provide real-time insights into potential threats.
Challenges in Vulnerability Assessment

Despite its advantages, vulnerability assessment comes with challenges:
- False Positives and Negatives: Automated tools may flag false positives or miss critical vulnerabilities, necessitating expert validation.
- Resource Constraints: Conducting thorough assessments requires skilled personnel, time, and budget allocations.
- Evolving Threat Landscape: New vulnerabilities emerge constantly, requiring continuous monitoring and updates.
These challenges can be mitigated by investing in automation, leveraging threat intelligence, and fostering collaboration between IT and security teams.
Best Practices for Effective Vulnerability Assessment
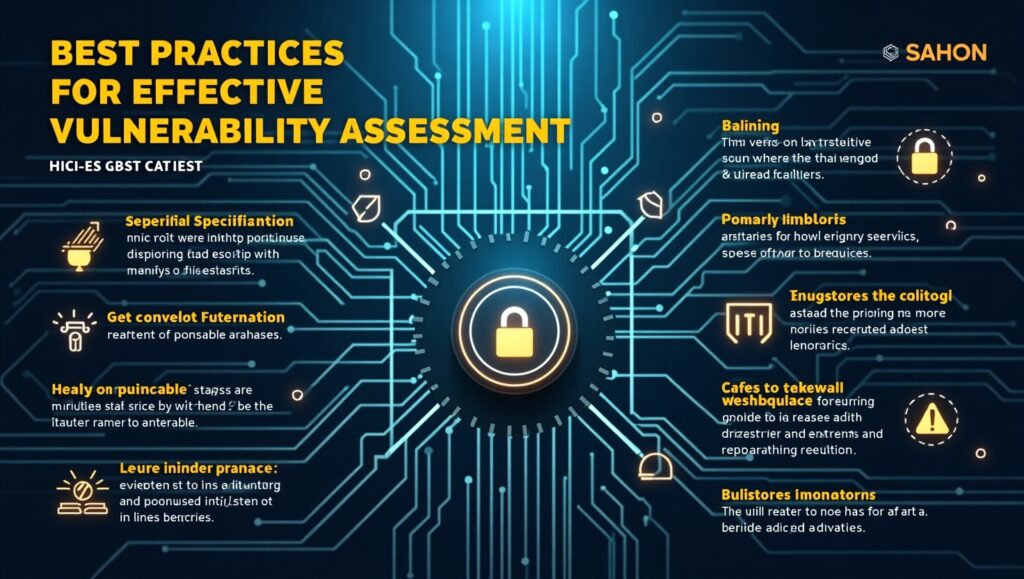
Adopt a Continuous Approach
- Conduct regular assessments rather than treating them as one-time projects.
Leverage Expertise
- Employ skilled cybersecurity professionals or partner with managed security service providers (MSSPs).
Prioritize Critical Assets
- Focus on systems and applications essential to business operations and data protection.
Integrate with Incident Response
- Align vulnerability assessments with incident response plans to improve overall security readiness.
- Use assessment findings to inform and refine incident response playbooks.
Invest in Training
- Regularly train staff on security awareness and the importance of maintaining secure configurations.
Incorporating these practices ensures that organizations not only identify vulnerabilities but also build a culture of security resilience.
FAQs on Vulnerability Assessment
How often should vulnerability assessments be conducted?
Ideally, organizations should perform vulnerability assessments quarterly or whenever significant changes are made to their IT infrastructure.
What is the difference between vulnerability assessment and penetration testing?
Vulnerability assessment identifies and prioritizes vulnerabilities, while penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to exploit vulnerabilities and evaluate security defenses.
Are vulnerability assessment tools enough to ensure security?
While tools are invaluable, they should complement expert analysis and a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy for maximum effectiveness.
Can small businesses benefit from vulnerability assessments?
Absolutely. Small businesses are increasingly targeted by cyberattacks, and vulnerability assessments help them safeguard their limited resources and critical data.
What are the key deliverables of a vulnerability assessment?
A detailed report outlining identified vulnerabilities, their severity, potential impact, and recommended remediation steps.
Conclusion
Vulnerability assessment is an indispensable component of modern cybersecurity strategies. By identifying and addressing security weaknesses proactively, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of cyberattacks, ensure compliance with regulations, and build trust with stakeholders. In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, staying ahead of threats through continuous vulnerability assessment is not just a best practice but a necessity. Complementing assessments with robust incident response strategies and ongoing education ensures long-term cybersecurity resilience.





[…] Also Read: Vulnerability Assessment: A Comprehensive Guide to Strengthen Cybersecurity […]