Table of Contents
Introduction
Building a high-performance DIY drone requires selecting the right components to ensure smooth, efficient, and stable flight. From motors to batteries, every part plays a crucial role in the drone’s performance. This guide will walk you through the essential components required for constructing a high-performance drone and how to choose the best options for your needs.
If you’re new to drone building and want a comprehensive guide, check out our article: How to Build a Drone from Scratch: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide.
Essential Components for a High-Performance DIY Drone
Frame
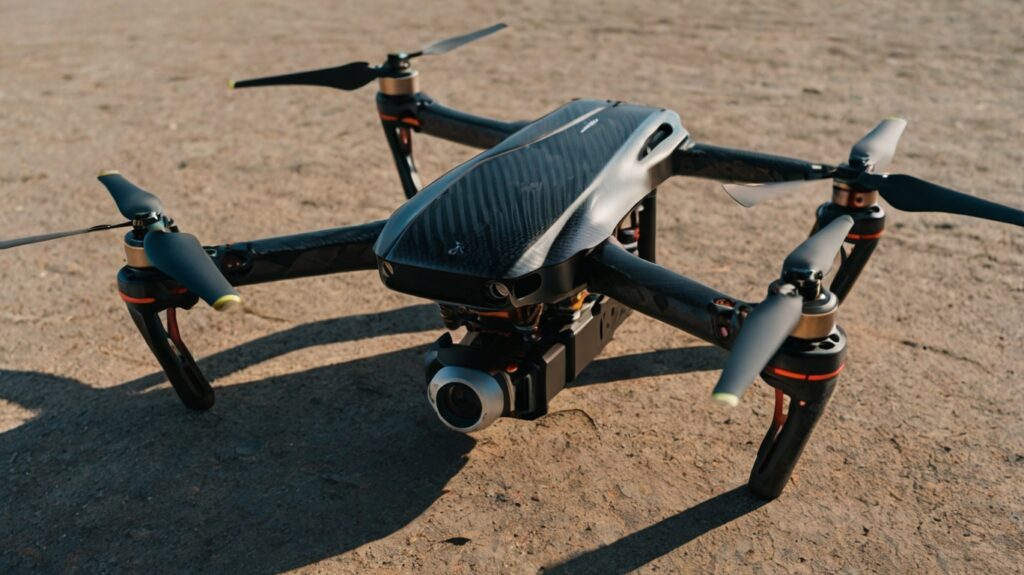

The frame is the central structure of a drone, providing the physical platform to mount all other components. Its design and material choice are crucial in determining the drone’s overall weight, strength, and durability. When building a high-performance DIY drone, selecting the right frame ensures better flight performance, increased stability, and greater longevity.
- Material Choices:
- Carbon Fiber: Carbon fiber is the preferred material for high-performance drones. It is lightweight, yet exceptionally strong, which makes it perfect for racing and FPV drones where minimizing weight while maximizing durability is key. Carbon fiber also has the advantage of being rigid, which helps in reducing unwanted vibrations that could affect the drone’s stability and the quality of aerial footage.
- Aluminum: Aluminum frames are generally heavier than carbon fiber but are more affordable. They are highly durable and offer good protection to the drone’s components, making them suitable for more general-purpose drones. However, the added weight may negatively impact flight time and speed compared to carbon fiber frames.
- Plastic (Polycarbonate or ABS): Plastic frames are often used for beginner drones due to their affordability. However, they are not as durable or light as carbon fiber, making them less ideal for high-performance builds.
- Size Considerations:
- Racing Drones: Racing drones typically use smaller frames, usually between 180mm to 250mm in diagonal motor-to-motor measurement. These compact sizes allow for faster acceleration and maneuverability, which are essential for racing.
- Aerial Photography Drones: For drones designed for aerial photography or cinematography, larger frames are needed to accommodate cameras, gimbals, and other accessories. Frames in the range of 250mm to 500mm are typical, allowing for additional space and stability.
- Long-Range Drones: If you’re building a drone for long-distance flying or mapping, you’ll need a frame that can support larger, more powerful motors and batteries while maintaining balance and efficiency. These frames often range from 300mm to 450mm in size.
- Frame Shape:
- X-Frame: Most high-performance drones use an X-frame design, where arms extend outward at 45-degree angles from a central body. This design provides better flight stability and control, especially at high speeds, and is a common choice for racing and FPV drones.
- H-Frame: H-frame designs are less common but offer extra stability, particularly for aerial photography drones where smooth flight is essential for capturing high-quality footage. The wider structure provides additional balance but may sacrifice some agility.
- Dead Cat Frame: This frame design is popular for drones intended for aerial photography, as it allows for better camera angles and clearer shots by positioning the camera more centrally. It’s more stable than an X-frame and minimizes the chances of propeller obstruction in the footage.
- Weight Considerations: The weight of the frame significantly affects the overall performance of the drone. A lighter frame allows for longer flight times and faster speeds, but it must still be strong enough to protect sensitive components. Balancing weight and durability is key—an excessively heavy frame will require more power to lift, reducing efficiency and flight time.
- Customization and Upgrades: Many DIY drone builders opt for frames that allow for customization and upgrades. Modular frames that allow you to easily add or remove components like landing gear, camera mounts, or gimbals are ideal for those looking to tailor their drone to specific needs.
Motors
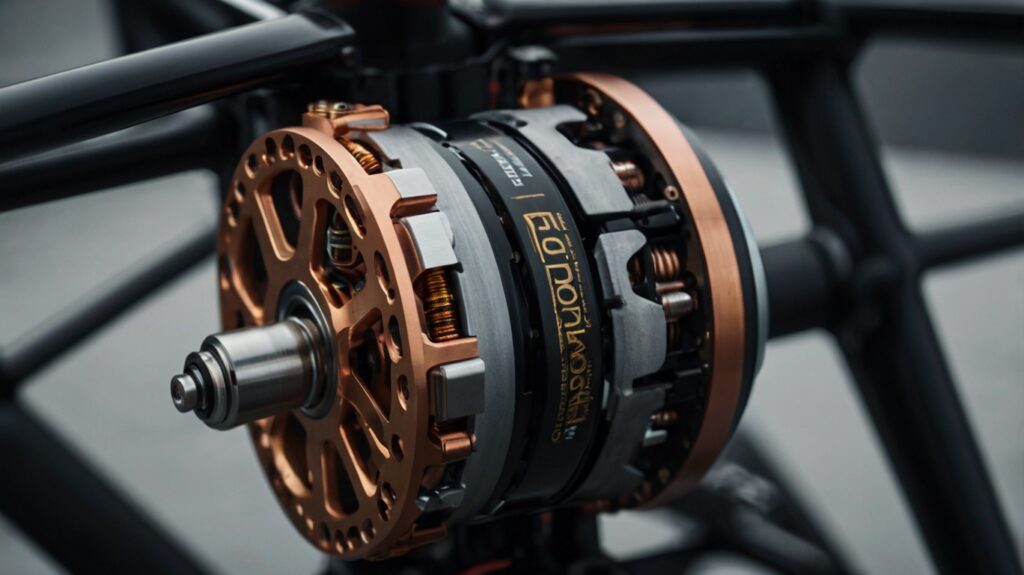

Motors are one of the most critical components of any drone, as they generate the thrust necessary for flight. Choosing the right motor is essential for achieving optimal performance in terms of power, efficiency, and control. For high-performance drones, brushless motors are the standard due to their superior efficiency, longevity, and power-to-weight ratio.
- Brushless Motors:
- Why They’re Preferred: Brushless motors are the top choice for high-performance drones because they offer several advantages over brushed motors, including greater efficiency, longer lifespan, and higher power output. Unlike brushed motors, which have brushes that wear down over time and create friction, brushless motors use electromagnetic fields to rotate the rotor, resulting in less wear and tear and more consistent performance. This efficiency allows for better battery life, faster speeds, and smoother flight characteristics.
- Durability: The absence of brushes in brushless motors means there is less maintenance required, and they can handle higher speeds and workloads without overheating. This is particularly important in high-performance applications like drone racing, where motors are subjected to intense stress during rapid maneuvers.
- Control and Precision: Brushless motors provide more precise control over the drone, which is especially important for tasks such as racing or cinematography, where stability and responsiveness are paramount.
- Motor Specifications: When selecting motors for your DIY drone, it’s essential to match them with the drone’s frame size, weight, and intended use. Key specifications to consider include:
- KV Rating: The KV rating (kilovolt rating) of a motor indicates how many revolutions the motor will make per minute (RPM) for every volt applied to it. A higher KV rating generally means the motor will spin faster, which is ideal for racing drones that require quick acceleration and high speeds. However, higher KV motors also require larger, higher-pitch propellers to maintain efficiency. Lower KV motors, on the other hand, are better suited for heavier drones and those used for aerial photography, as they provide more torque at lower speeds.
- Example: A motor with a KV rating of 2300 would spin at 2300 RPM when 1 volt is applied. A motor with a KV rating of 1200 would be more suitable for heavy-lift drones or drones designed for stability and longer flight times.
- Motor Size: The motor size is usually represented by a four-digit number (e.g., 2206, 2306, 2507), where the first two digits indicate the motor’s width (in millimeters), and the last two digits indicate the motor’s height. Larger motors, such as 2507, provide greater thrust, which is necessary for larger drones that need to lift heavy payloads, like cameras or gimbals. Smaller motors, like 2204 or 2206, are better suited for lighter racing drones.
- Motor Mounting Pattern: Motors come in different mounting patterns, typically either 16x16mm or 19x19mm. Make sure to choose motors that match your drone’s frame mounting holes. This is a critical compatibility factor to avoid issues during assembly.
- Power Requirements and Efficiency:
- Thrust-to-Weight Ratio: A key performance indicator for motors is the thrust-to-weight ratio, which represents how much thrust the motor can generate relative to its weight. For high-performance drones, you want a motor that can generate sufficient thrust without adding unnecessary weight.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of a motor determines how well it converts battery power into thrust. Highly efficient motors help extend flight times and reduce the load on the battery. High-efficiency motors tend to be made from better quality materials, such as high-grade copper windings and high-quality bearings.
- KV Rating: The KV rating (kilovolt rating) of a motor indicates how many revolutions the motor will make per minute (RPM) for every volt applied to it. A higher KV rating generally means the motor will spin faster, which is ideal for racing drones that require quick acceleration and high speeds. However, higher KV motors also require larger, higher-pitch propellers to maintain efficiency. Lower KV motors, on the other hand, are better suited for heavier drones and those used for aerial photography, as they provide more torque at lower speeds.
- Motor Features and Materials:
- Winding Type: The winding type in a motor (e.g., 12N14P, 14N16P) affects the motor’s efficiency and power delivery. More poles (P) typically result in smoother power output and better efficiency.
- Cooling and Bearings: Motors with high-quality bearings and cooling features (such as vented motors) are less prone to overheating, especially in high-stress situations like racing. Consider motors with high-quality ceramic or steel bearings for better longevity and reduced wear.
- Magnet Type: The magnets used in the motor affect its performance. Neodymium magnets are commonly used in high-performance motors for their strength and efficiency, but they also increase the motor’s cost.
- Motor-Propeller Compatibility:
- The motor and propeller combination significantly impacts the overall performance of the drone. Larger motors, such as those with a 2208 or 2507 designation, typically require larger propellers to generate sufficient thrust. Smaller motors, like a 2204, are paired with smaller propellers to maintain efficient power delivery.
- Propeller Size and Pitch: The motor’s KV rating helps determine the ideal propeller size and pitch. High KV motors work well with smaller, higher-pitch propellers, which are suitable for racing drones that require quick acceleration. Lower KV motors perform best with larger, lower-pitch propellers, which provide more lift and stability for aerial photography drones.
- Motor Brands and Quality: Some top brands for high-performance drone motors include:
- T-Motor: Known for their reliability and precision, T-Motor motors are often used in professional-grade drones and racing drones.
- Emax: Emax motors are popular among hobbyists for their excellent performance and reasonable pricing. They offer a wide range of motors suitable for different drone sizes and applications.
- SunnySky: Known for making efficient, high-quality motors for racing and commercial drones.
In conclusion, selecting the right motor is essential for achieving the desired performance in your DIY drone. Brushless motors provide the best power, efficiency, and durability, and matching the motor’s specifications with the drone’s intended use—whether it’s for racing, aerial photography, or heavy lifting—is crucial for optimal results. By considering the motor’s KV rating, size, thrust capabilities, and compatibility with the propellers and frame, you can build a high-performance drone tailored to your needs.
Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs)
ESCs regulate the speed of the motors and are crucial for controlling the drone’s stability.
- Importance: ESCs ensure smooth motor transitions and precise control over the drone’s flight.
- Recommended Specs: Opt for ESCs that match your motor specifications, and ensure they support high-frequency firmware options for better performance and responsiveness.
Flight Controller
The flight controller is responsible for stabilizing the drone during flight.
- Role: It processes inputs from the pilot and sensors to adjust the motors, keeping the drone stable.
- Popular Options: Some well-known flight controllers include the Betaflight, Pixhawk, and DJI Naza systems. Look for features like gyro and accelerometer integration for smooth flight control.
Propellers
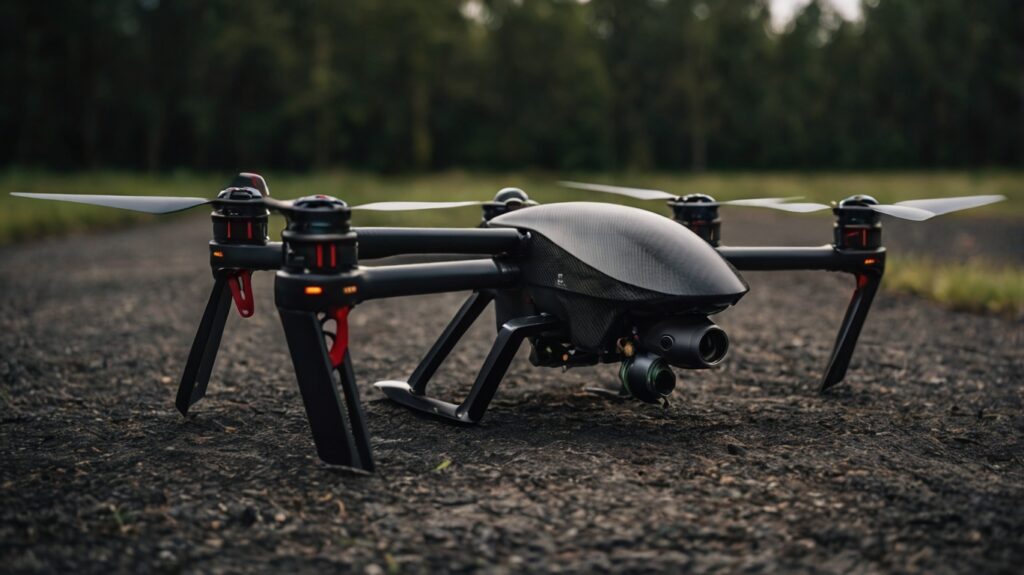

Propellers convert the motor’s power into lift, making them an integral part of the drone’s performance.
- Material: Carbon fiber propellers are more durable and efficient compared to plastic, making them ideal for high-performance drones.
- Size and Pitch: Ensure the propeller size and pitch match the motor’s capabilities to achieve the best lift-to-thrust ratio for your drone.
Battery
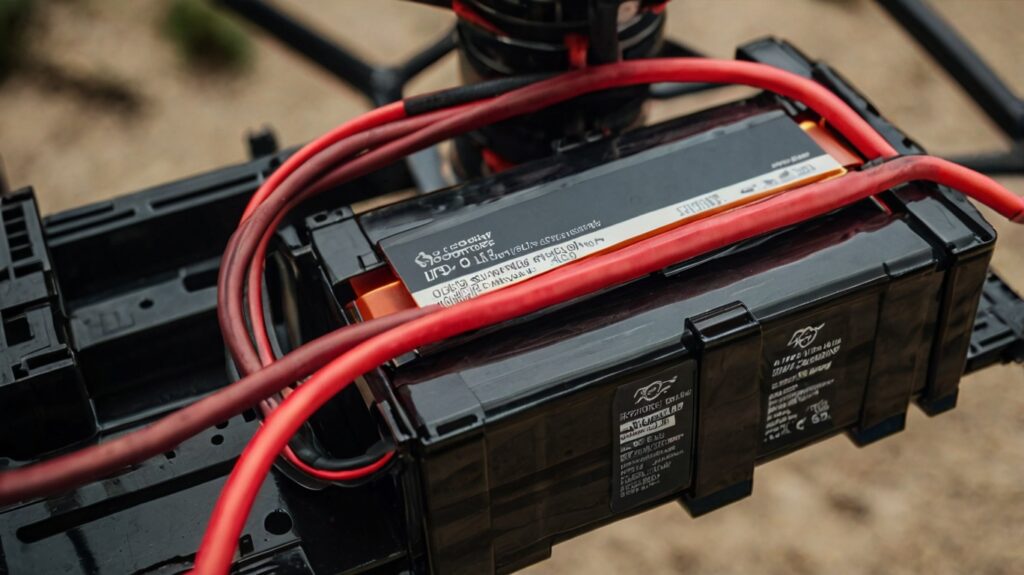

Batteries power the drone and determine its flight time and weight.
- Types of Batteries: LiPo (Lithium-Polymer) batteries are the standard for high-performance drones due to their high energy density and light weight.
- Weight Considerations: The battery should be chosen based on the drone’s total weight and required flight time. A larger battery provides more flight time but also increases weight, which can impact performance.
Remote Control System
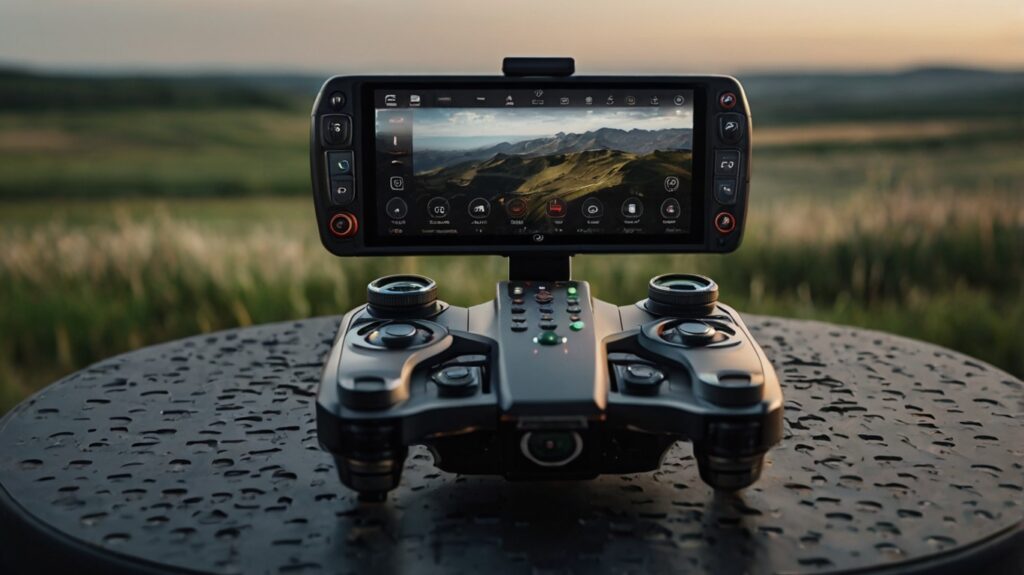

The remote control system is the communication link between the pilot and the drone. It enables the pilot to control the drone’s movement and functions, making it a vital component for any high-performance DIY drone build. A well-chosen remote control system ensures responsive and stable flight, which is particularly important in racing drones or professional aerial photography.
- Components of a Remote Control System: A remote control system typically consists of two main components: the transmitter (the handheld controller used by the pilot) and the receiver (the component installed on the drone that receives signals from the transmitter).
- Transmitter (Controller): The transmitter is the device the pilot holds, and it sends control signals to the drone. It can have different types of controls, including:
- Throttle (Acceleration): Controls the drone’s altitude.
- Yaw (Rotation): Controls the drone’s left and right rotation.
- Pitch (Forward/Backward): Controls the drone’s movement forward or backward.
- Roll (Left/Right): Controls the drone’s movement left or right.
- Additional Buttons and Knobs: Many transmitters include buttons for activating specific functions, such as camera control, gimbal stabilization, or special modes (like return-to-home or fail-safe settings).
- Receiver: The receiver is mounted on the drone and is responsible for receiving control signals from the transmitter. The receiver converts these signals into actions that adjust the drone’s flight controller, motors, and other components.
- Transmitter (Controller): The transmitter is the device the pilot holds, and it sends control signals to the drone. It can have different types of controls, including:
- Range and Signal Quality:
- Range: One of the most important aspects of any remote control system is its range, which refers to how far the pilot can control the drone. For racing drones, range may not be as critical as agility and response time, but for long-range drone flying (such as mapping or surveying), having a remote control system with an extended range is vital. Typical remote control systems offer ranges anywhere from 1 km to over 30 km, depending on the technology used.
- Signal Quality: The quality of the signal is equally important, especially for long-range flights or in environments with lots of interference. Modern systems use frequency hopping technology or dual-frequency channels (2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz) to avoid interference, providing more stable connections.
- Frequency and Channel:
- Most modern remote control systems operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency range, which offers good range and reliability. However, some systems also offer the option to switch to the 5.8 GHz frequency to avoid interference from other devices in crowded areas. Higher frequencies generally provide faster data transfer, but they may be more prone to signal loss at greater distances.
- Channels: A transmitter typically sends signals through multiple channels. Commonly, 4-6 channels are used in standard drones for controlling basic flight functions. More advanced systems may have 8 or more channels to support additional features such as camera gimbal control or additional flight modes. Each channel can control a specific action or component of the drone.
- Transmission Protocol: The transmission protocol determines how data is communicated between the transmitter and receiver. Some of the most popular protocols include:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): An older, but still common, signal transmission method. PWM is less complex but can suffer from latency and signal interference.
- SBUS: A newer digital protocol that allows for faster, more reliable communication with less latency compared to PWM. It supports a greater number of channels and is commonly used in modern drones.
- CRSF (Crossfire): Known for providing very low latency and high range, Crossfire is particularly popular among long-range pilots and racing enthusiasts. It’s often paired with specialized long-range receivers and offers an extremely reliable link, even in areas with lots of interference.
- Ergonomics and Features:
- Build Quality and Comfort: The comfort and ergonomics of the transmitter are essential, especially for extended flights. Look for controllers with adjustable grips, lightweight materials, and easy-to-reach switches and buttons. Some transmitters come with customizable gimbals (the sticks that control yaw, pitch, and roll), allowing pilots to fine-tune the feel of the controls to suit their flying style.
- Display and Feedback: Advanced transmitters often come with built-in displays to provide real-time telemetry data such as battery levels, GPS coordinates, signal strength, and even FPV camera feed. This can be particularly helpful for long-range or FPV (first-person view) flights, allowing pilots to monitor flight performance and make adjustments as needed.
- Customizable Controls: High-end transmitters allow you to map specific functions to custom switches, providing flexibility for pilots who want to optimize their controls for specific flight modes or operations.
- Flight Modes: Many modern remote control systems offer multiple flight modes to enhance the user experience and improve flight control. Some key modes to consider include:
- Stabilized Mode: This mode helps keep the drone stable by using the flight controller to adjust motor speeds and control the drone’s movement. It’s ideal for beginners or when smooth, stable flight is required.
- Acro Mode: Used by more advanced pilots, acro mode allows for manual control of the drone without automatic stabilization. It is often preferred in racing and freestyle flying, as it offers greater maneuverability and control.
- GPS Hold or RTH (Return-to-Home): GPS-based modes allow the drone to hold its position in the air or return to its launch point automatically if the signal is lost or the battery runs low. This is particularly useful for long-range flights and adds an extra layer of safety.
- Altitude Hold: This mode allows the drone to maintain a constant altitude, which can be beneficial for aerial photography or videography, ensuring smooth footage.
- Popular Remote Control Systems: There are several well-regarded remote control systems available for high-performance drones:
- FrSky Taranis X9D Plus: A widely popular transmitter in the drone community, known for its customization options, reliability, and large range. It’s commonly used by drone racing pilots and enthusiasts.
- Spektrum DX8e: Known for its solid build quality and excellent range, this transmitter is used by many drone pilots, from beginners to experts. It supports multiple receivers and offers a broad range of features.
- Radiomaster TX16S: A versatile transmitter that supports multiple protocols and offers a large screen, customizable controls, and excellent build quality. It is often favored by drone racers and FPV enthusiasts for its flexibility and ease of use.
- DJI Remote Controllers (for DJI Drones): While primarily used with DJI drones, DJI’s remote controllers are renowned for their user-friendly interface, integrated display, and seamless compatibility with DJI’s flight systems, making them a top choice for aerial photographers and videographers.
- Compatibility with Flight Controller: Ensure that the remote control system you select is compatible with your flight controller. Different flight controllers may require specific types of receivers or support different communication protocols (e.g., SBUS, PPM, PWM). Most high-performance flight controllers are compatible with a wide range of transmitters, but it’s always good practice to double-check compatibility before purchasing.
Additional Components for Advanced Features
Power Distribution Board (PDB)
The PDB manages the distribution of power from the battery to various components, ensuring balanced power flow for smooth operation.
FPV System (Camera, vTx, vRx)
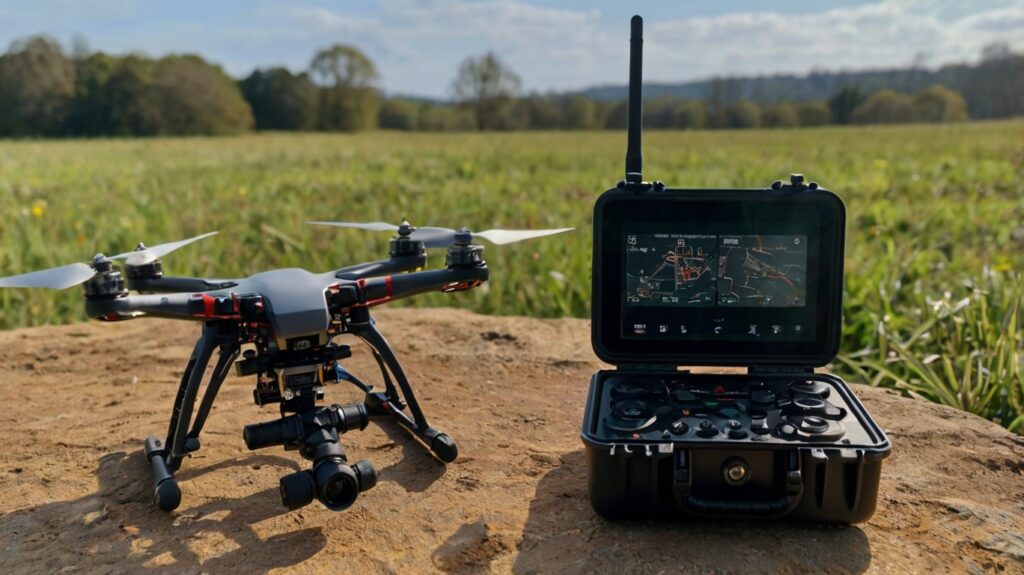

For FPV (First-Person View) drones, the camera, video transmitter (vTx), and video receiver (vRx) are essential for transmitting real-time footage to the pilot.
Optional Accessories
- Landing Gear: Adds stability during takeoff and landing.
- Gimbals: For aerial photography drones, gimbals help stabilize the camera, reducing vibrations and ensuring smooth footage.
- Sensors: GPS, obstacle avoidance, and other sensors enhance the drone’s functionality and safety.
Compatibility and Testing
Ensuring all components are compatible is crucial for the success of your build.
- Compatibility: Double-check specifications and connectors to ensure all parts work seamlessly together.
- Testing Tips: During assembly, test each component individually before completing the build. This ensures everything is functioning properly and minimizes issues during flight.
Final Thoughts
Building a high-performance DIY drone requires careful selection of components that suit your specific needs. Whether you’re building for racing or aerial photography, each component— from motors to batteries— plays a vital role in your drone’s success. Remember to test compatibility and ensure every part meets the demands of your intended use for optimal performance.




[…] For a detailed guide on selecting the best parts for your high-performance drone, check out High-Performance DIY Drone: A Technical Guide to Choosing the Best Parts. […]
[…] Also Read: High-Performance DIY Drone: A Technical Guide to Choosing the Best Parts […]