Ensuring the security of one’s home is a fundamental concern for homeowners. Opting for a DIY home security system presents an economically viable and highly customizable alternative to traditional professionally installed systems. This comprehensive guide delineates the design, installation, and optimization of a DIY home security system tailored to individual requirements.
Also Read: Portable Air Quality Monitor Review: Is It Worth the Investment in 2025?
Table of Contents
Why Opt for a DIY Home Security System?
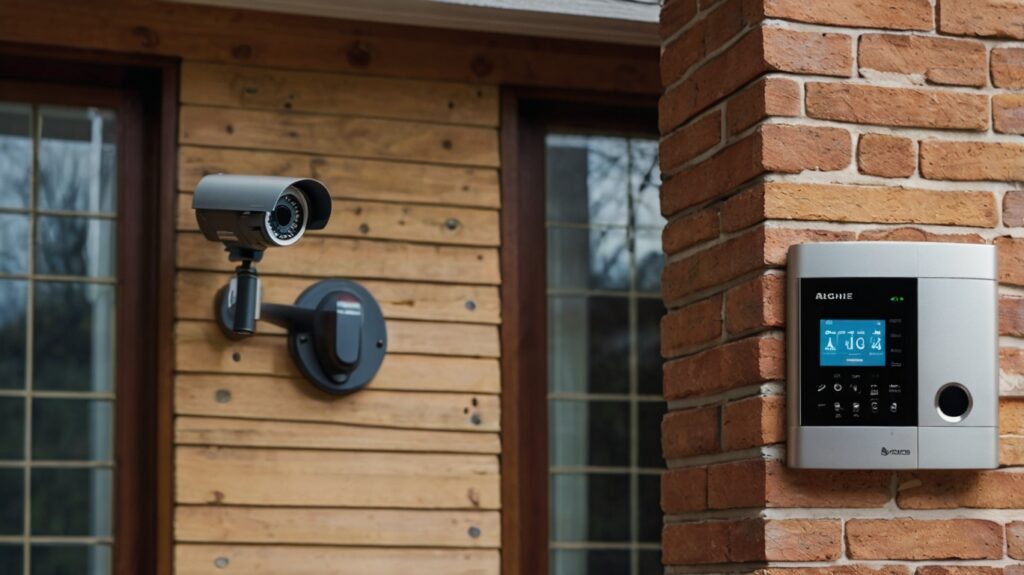

The increasing prevalence of DIY home security systems can be attributed to their affordability, adaptability, and user-centric design. Below are key advantages of this approach:
- Economic Efficiency: Substantially reduce costs by circumventing professional installation and subscription fees.
- Customizability: Adapt the system’s configuration to align with the specific architectural layout and security needs of your home.
- User Accessibility: Engineered for intuitive installation and straightforward operation.
- Scalability: Facilitate incremental enhancements by integrating additional components over time.
Core Components of a DIY Home Security System

An efficacious DIY security system comprises several critical elements:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Control Panel | Functions as the central command center, coordinating all connected devices for management. |
| Door and Window Sensors | Serve as the first line of defense, detecting unauthorized access through doors or windows. |
| Motion Detectors | Identify unpermitted movement within designated zones when strategically positioned. |
| Security Cameras | Provide real-time surveillance and recording; available in indoor/outdoor and wired/wireless options. |
| Alarm Sirens | Emit high-decibel sounds to deter intruders and alert nearby individuals. |
| Smart Locks | Replace traditional locks with keyless entry and advanced access control capabilities. |
| Mobile App Integration | Enable remote monitoring and control of the security infrastructure via mobile applications. |
Strategic Planning for a DIY Home Security System

1. Conduct a Security Assessment
Begin by thoroughly evaluating your home to identify potential vulnerabilities. Analyze entry points such as doors and windows, high-traffic areas, and any external threats that could compromise security. Consider environmental factors, such as lighting and visibility, which might impact the effectiveness of your system.
2. Select an Appropriate System
Choose a security system that meets your financial constraints while addressing your functional needs. When evaluating options, assess the scalability, ease of use, and integration capabilities. Notable systems include:
- SimpliSafe: Esteemed for its cost-effectiveness and intuitive design, SimpliSafe offers optional professional monitoring for added security.
- Ring Alarm: This system excels in integrating seamlessly with Amazon Alexa devices, making it an excellent choice for smart home enthusiasts.
- Abode Smart Security Kit: Designed for compatibility with existing smart home ecosystems, Abode offers extensive customization and advanced features.
Additionally, consider reading user reviews and consulting product specifications to ensure the chosen system aligns with your specific requirements.
3. Develop a Layout Plan
Draft a detailed schematic representation of your home to determine the optimal placement of security components. Mark critical areas such as entry points, blind spots, and high-traffic zones. Account for environmental factors like obstructions or power sources that might influence installation. This strategic approach ensures maximum coverage and operational efficiency of your security system.
Installation Protocol for a DIY Home Security System
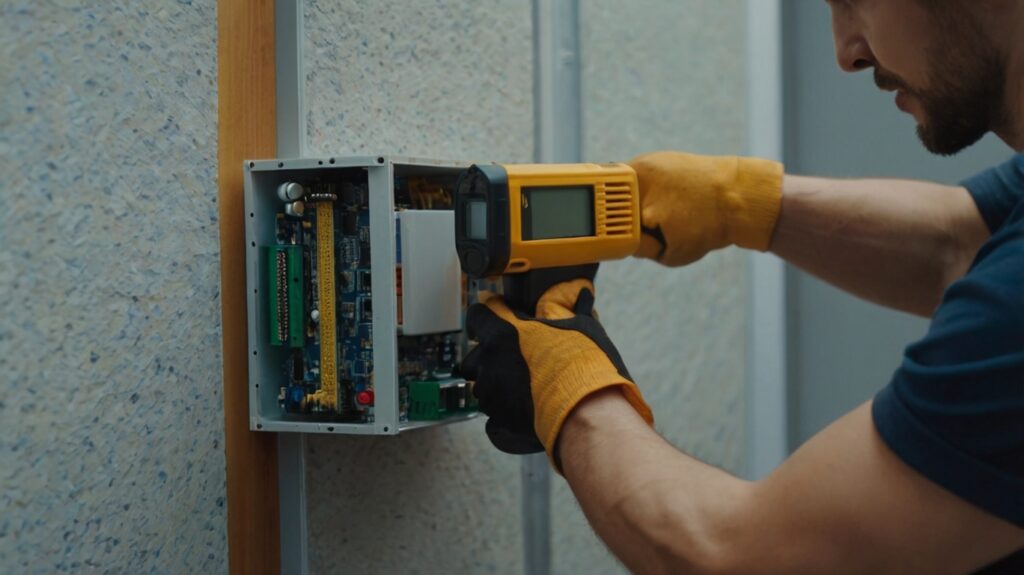

Step 1: Verify and Organize Components
Before initiating the installation process, thoroughly inspect all components to ensure they are present and in operational condition. Cross-check the items against the provided inventory list to confirm completeness. If any parts are missing or damaged, contact the manufacturer immediately for replacements.
Step 2: Install Door and Window Sensors
- Begin by identifying suitable locations for the sensors on doors and windows. Ensure these areas are free of dust and debris for proper adhesion.
- Secure the sensors using the adhesive strips or screws included in the kit. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid misalignment.
- Align the sensor and magnet components accurately, ensuring they connect seamlessly when the door or window is closed. Test each sensor to verify functionality before moving to the next installation.
Step 3: Position Motion Detectors
- Identify optimal positions for motion detectors, typically in corners of rooms or hallways at a height of 6-8 feet. This placement maximizes coverage while minimizing blind spots.
- Use the mounting hardware provided to securely attach the detectors. Adjust their angles to cover the intended area effectively.
- Configure sensitivity settings to reduce false alarms caused by pets or environmental factors. Test the detectors by simulating movement within their range.
Step 4: Deploy Security Cameras
- Strategically position cameras at key entry points and high-traffic zones. Ensure they are placed at a height that prevents tampering while providing a clear field of view.
- For outdoor cameras, verify they are weatherproof and positioned to avoid glare or obstructions. Use cable management solutions for wired cameras to maintain a clean setup.
- Connect wireless cameras to the home’s Wi-Fi network and test their video feed for clarity and stability. Adjust angles as necessary for optimal surveillance.
Step 5: Configure the Control Panel
- Select an accessible location near a primary entry point for the control panel. This ensures ease of use while maintaining security.
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to integrate all sensors, cameras, and detectors with the control panel. Use the system’s mobile app, if available, to streamline configuration.
- Set user profiles, notification preferences, and system passwords to enhance security and usability.
Step 6: Conduct System Testing
- Simulate various security scenarios to verify the operational integrity of each component. For example, open doors and windows to test sensors, walk through monitored areas to trigger motion detectors, and review camera feeds for real-time accuracy.
- Document any issues encountered during testing and address them promptly. Ensure the system functions seamlessly before relying on it for full-time security.
Enhancing the Efficacy of Your DIY Security System

Smart Device Integration
Enhance your security system by integrating it with a broader range of smart home devices. Consider linking it to automated lighting systems that can simulate occupancy when you’re away, or to smart thermostats that adjust based on security alerts. Voice-controlled assistants, such as Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant, can further streamline system management, allowing for hands-free operation and real-time updates on security status. Additionally, smart plugs and appliances can be connected to improve energy efficiency and overall convenience.
Routine Maintenance
To ensure long-term reliability, develop a regular maintenance schedule. Inspect all components, including sensors, cameras, and control panels, for physical damage or wear. Test the system’s connectivity and responsiveness by triggering alerts and reviewing notifications. Replace batteries in wireless devices at least annually, or as recommended by the manufacturer, to prevent unexpected failures. Keep software and firmware up to date to benefit from the latest security enhancements and features. Document each maintenance check to track performance over time.
Incorporate Advanced Features
Capitalize on cutting-edge advancements in home security technology to elevate your system’s effectiveness. Integrate facial recognition to differentiate between family members and potential intruders, minimizing false alarms. AI-driven analytics can analyze patterns of activity, providing insights into unusual behavior and optimizing system responses. Advanced motion detectors equipped with heat and sound sensors can further refine detection accuracy. For added security, consider integrating biometric locks or encrypted data storage for recorded footage, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected.
FAQs
What is the typical cost of a DIY home security system?
Depending on the brand and components, costs generally range from $200 to $600 for a standard setup.
Is professional monitoring necessary?
Professional monitoring is optional; many systems support self-monitoring via mobile applications.
Can a DIY system be installed in a rental property?
Yes, DIY systems are typically portable and non-invasive, making them well-suited for rental accommodations.
What is the expected lifespan of a DIY home security system?
With consistent maintenance, most systems remain functional for 5-10 years. Regular updates and component replacements can extend longevity.
Are DIY systems comparable to professional setups in effectiveness?
When meticulously planned and maintained, DIY systems can deliver security measures on par with professional installations.
Conclusion
Implementing a DIY home security system is an intellectually rewarding endeavor that not only bolsters residential safety but also instills a profound sense of peace of mind. This approach empowers homeowners to take control of their security measures, tailoring solutions to their specific needs and preferences. By meticulously selecting high-quality components, devising a comprehensive and strategic installation plan, and committing to regular maintenance, individuals can achieve a robust and reliable security solution.
Moreover, the process of building and optimizing such a system fosters a deeper understanding of modern security technologies and their applications. With careful planning and ongoing attention, a DIY home security system becomes a sustainable, cost-effective, and highly customizable way to safeguard one’s home and loved ones against potential threats.




[…] Also Read: Creating a DIY Home Security System: A Complete Guide for 2025 […]