Table of Contents
Introduction
PolyJet technology is revolutionizing the world of 3D printing with its ability to combine multiple material properties into a single part. Whether it’s blending rigid and flexible materials or adding color variations, PolyJet allows for precise multi-material and multi-property output. This innovation has opened up new possibilities for design, prototyping, and production across various industries.
What is PolyJet Technology?
PolyJet technology is an advanced 3D printing method that works similarly to traditional inkjet printing, but instead of ink, it jets tiny droplets of liquid photopolymer onto a build tray. These photopolymers are instantly cured (solidified) using ultraviolet (UV) light, layer by layer, to form precise, detailed, and multi-material parts.
Key Features of PolyJet Technology
- Multi-Material Printing:
PolyJet stands out because it can combine different materials in a single print job. For instance, it can print both rigid and flexible sections, translucent and opaque areas, or even blend materials to create intermediate properties (e.g., semi-rigid). - High Resolution and Accuracy:
PolyJet technology produces ultra-fine layer thicknesses as thin as 16 microns (0.016 mm). This allows for highly detailed parts with smooth surfaces, sharp edges, and intricate features. - Wide Range of Materials:
- Rigid Materials: Suitable for hard parts, casings, or solid prototypes.
- Flexible Materials: Rubber-like photopolymers for soft-touch parts like gaskets or grips.
- Transparent Materials: For applications requiring clear or semi-transparent sections, such as lenses.
- Color Options: Full-color photopolymers allow vibrant, realistic prototypes.
- Digital Materials: Blending multiple base materials enables customized properties like varying shore hardness (softness/stiffness).
- Support Material Integration:
PolyJet printers use a special gel-like support material that can be easily removed, even for complex geometries, ensuring smooth surfaces and accurate detailing.
Here’s an expanded version of the “How Does PolyJet Work?” section to add more depth and detail:
How Does PolyJet Work?
PolyJet technology is an additive manufacturing process that builds parts layer by layer by jetting liquid photopolymer droplets and instantly curing them with UV light. This method allows for the creation of highly detailed, multi-material, and full-color 3D-printed parts. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of how the PolyJet process works:
1. Material Jetting
PolyJet technology uses a print head, similar to that of an inkjet printer, equipped with multiple nozzles. These nozzles precisely jet microscopic droplets of liquid photopolymer materials onto a build tray.
- The print head can jet different materials simultaneously, including rigid, flexible, opaque, transparent, and full-color photopolymers.
- The jetting process ensures accuracy, enabling the creation of highly detailed geometries and textures.
2. Layer-by-Layer Curing with UV Light
Once the photopolymer droplets are deposited onto the build tray, they are immediately solidified (cured) using ultraviolet (UV) light.
- This curing happens instantly after each layer is jetted, ensuring the material hardens and maintains its precision.
- Since curing is immediate, the process avoids smearing or deformation, making it ideal for parts requiring fine detail.
3. Multi-Material and Color Integration
What sets PolyJet apart is its ability to combine multiple materials and colors in a single print job:
- Material Blending: PolyJet allows materials to be blended during printing to create digital materials with customized properties, such as varying levels of stiffness or softness (shore hardness).
- Multi-Color Printing: PolyJet printers can print in full color by combining different photopolymers, enabling realistic prototypes with vibrant hues, gradients, and textures.
- Property Control: Each area of the part can be assigned specific properties. For example, a part can have a rigid core for strength, a flexible outer layer for grip, and transparent areas for visual appeal—all in one build.
4. Support Material for Complex Geometries
PolyJet technology uses a gel-like support material to print overhanging structures, intricate internal cavities, or complex designs.
- The support material is deposited alongside the build material during printing.
- Once the print is complete, the support material is removed using water jets or hand tools, leaving a smooth and clean surface without damaging delicate features.
5. Build Process Completion
Once all the layers are jetted, cured, and support materials are removed, the finished part is ready. Post-processing is minimal because PolyJet technology produces parts with:
- Ultra-smooth surfaces.
- High accuracy (up to 16-micron layer resolution).
- Full-color and multi-material combinations, eliminating the need for painting or assembly.
Key Highlights of the PolyJet Process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Jetting | Microscopic droplets of photopolymer are jetted onto the build tray through multiple nozzles. |
| UV Curing | Each layer is solidified immediately using UV light for accuracy and precision. |
| Material Blending | Multiple materials and colors are combined to produce custom digital materials. |
| Support Material | A removable gel-like support ensures complex geometries and overhangs are printed perfectly. |
| Post-Processing | Support removal is simple, and parts require minimal finishing due to their high-quality surface. |
Why is PolyJet So Precise?
PolyJet achieves such high precision because of:
- Layer Resolution: Each layer is as fine as 16 microns (0.016 mm), ensuring detailed textures and smooth surfaces.
- Droplet Size: The tiny droplets allow intricate features to be created without losing structural integrity.
- Instant Curing: UV curing solidifies each layer immediately, ensuring the part doesn’t shift or deform during printing.
Why PolyJet is Ideal for Multi-Material Printing
PolyJet’s ability to print using multiple materials simultaneously makes it highly versatile. By allowing different materials to be deposited in specific areas of a single part, it enables engineers and designers to create prototypes or models that mimic real-world products.
For example:
- A model can have rigid housings alongside soft-touch grips.
- A single print can include transparent sections for windows and opaque sections for frames.
How PolyJet Achieves Multi-Material Properties
PolyJet’s unique ability to deliver multiple material properties in one part lies in its multi-material jetting process.
- Material Jetting: PolyJet printers can jet different photopolymers simultaneously during the build process.
- Digital Material Blending: By mixing two or more base resins, PolyJet creates “digital materials” that exhibit combined properties like varying stiffness, textures, and colors.
- Layer-by-Layer Property Integration: Each layer of the part can incorporate different materials, allowing for complex combinations like rigid cores with soft-touch surfaces.
For example:
- A prototype with rigid plastic housing and flexible rubberized grips.
- A model blending transparent and opaque regions to simulate real-world conditions.
Advantages of Multi-Material Printing
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Design Flexibility | Enables varied colors, textures, and material characteristics in a single part. |
| Reduced Assembly | Eliminates the need to assemble separate parts, saving time and cost. |
| Realistic Prototypes | Produces functional prototypes that closely mimic final end-use products. |
| Time Efficiency | Speeds up the prototyping process by producing multi-material parts in one go. |
Examples of PolyJet Technology in Action
PolyJet technology’s ability to combine multi-material and multi-color properties makes it incredibly versatile for various industries. From medical fields to consumer products, PolyJet is enabling innovation and realistic prototyping like never before. Here are some real-world examples of how PolyJet technology is applied:
1. Medical Devices and Anatomical Models
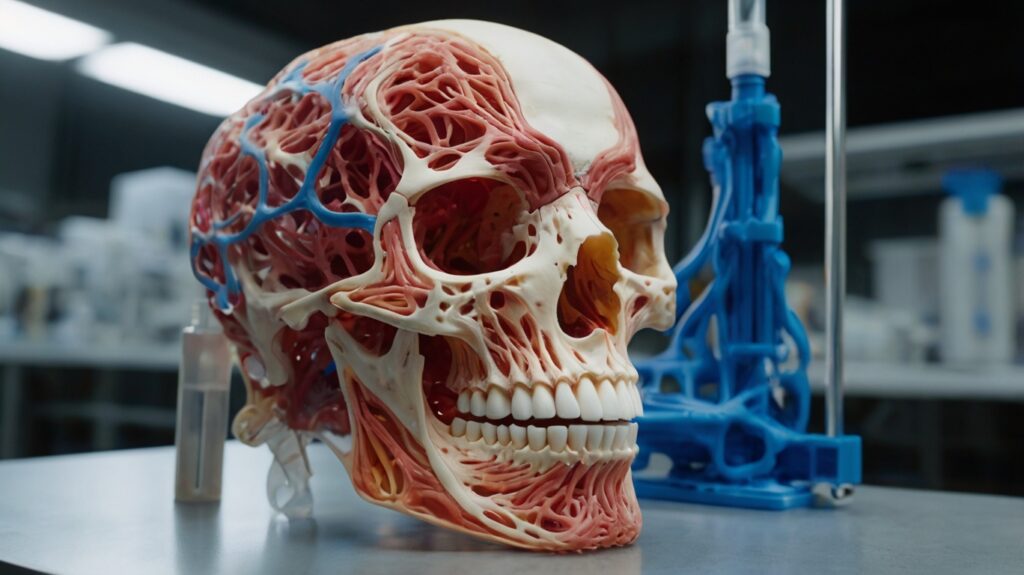
In the healthcare industry, PolyJet technology is widely used to create detailed anatomical models that aid in surgical planning, medical training, and diagnostics.
- Multi-Material Simulations: Models can combine rigid and soft materials to simulate bones, tissues, and veins with lifelike accuracy.
- Color-Coded Anatomy: Full-color photopolymers allow doctors to identify organs, blood vessels, and other features in distinct colors.
- Custom Implants and Prosthetics: PolyJet enables the creation of patient-specific prototypes for implants or prosthetics that fit precisely.
Example: A surgical team could practice a procedure on a 3D-printed model of a heart, featuring rigid walls for the ventricles and flexible materials for surrounding arteries, enhancing the precision of training.
2. Consumer Electronics Prototyping

For manufacturers in the consumer electronics space, PolyJet is a game-changer for producing high-fidelity prototypes that look and feel like final products.
- Functional Prototypes: Combine rigid plastic for casings with flexible materials for buttons or soft-touch grips.
- Realistic Design Validation: Transparent materials can be used for screens or covers, while color variations allow for realistic branding and labeling.
- Reduced Iteration Time: Multi-material printing enables engineers to validate designs quickly without assembling separate parts.
Example: A smartphone prototype could feature a rigid, glossy plastic housing with soft-touch flexible areas for buttons and a semi-transparent cover to simulate the display screen.
3. Automotive Design and Concept Models

PolyJet technology is heavily used in the automotive industry to create complex design models and functional prototypes.
- Detailed Concept Parts: Designers can print prototypes with intricate geometries, integrating rigid and flexible parts in a single build.
- Transparent Components: Parts like headlights, light covers, and windshields can be printed using clear photopolymers to test optical properties.
- Rubber-Like Features: Flexible materials enable the creation of soft seals, gaskets, or tires for testing purposes.
Example: An automotive company can 3D print a car dashboard prototype that includes rigid panel sections, flexible knobs, and transparent displays all in one seamless model.
4. Consumer Products and Packaging

PolyJet technology is ideal for designing and testing consumer products and packaging solutions, thanks to its ability to create realistic prototypes.
- Multi-Texture Models: Combine smooth, glossy surfaces with textured, rubber-like areas to simulate realistic touch and feel.
- Color Accuracy: Full-color printing ensures branding elements, logos, and labels are presented clearly for evaluation.
- Packaging Prototypes: Test packaging that blends transparency, rigidity, and flexible elements to validate both aesthetics and functionality.
Example: A prototype for a shampoo bottle can include a semi-translucent body, soft rubber grips on the sides, and color branding that accurately represents the final design.
5. Education and Training
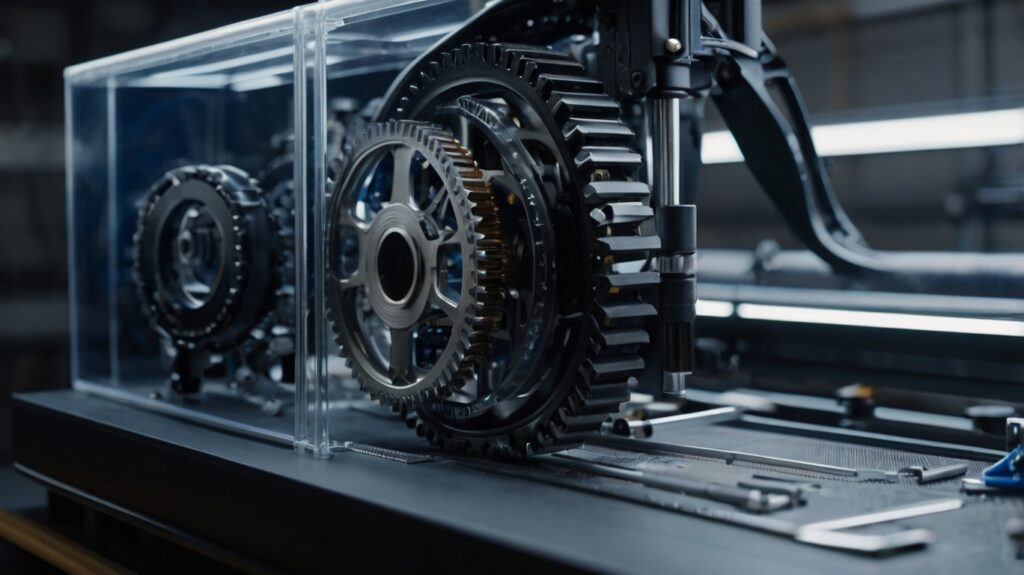
In educational settings, PolyJet enables the creation of interactive teaching tools and realistic models that enhance hands-on learning.
- Interactive Learning Aids: Print detailed mechanical models, biological structures, or engineering components for classroom use.
- Material Simulations: Different materials can highlight functional parts, such as rigid gears alongside soft, flexible belts.
- Color-Coded Learning Tools: Models can use color to differentiate parts, making complex structures easier to understand.
Example: Engineering students could use a 3D-printed mechanical assembly with transparent sections to observe internal moving parts, enhancing their understanding of mechanical systems
Conclusion
PolyJet technology has redefined the possibilities of 3D printing by enabling multi-material properties in a single part. Its ability to combine rigid, flexible, translucent, and colorful elements allows manufacturers and designers to achieve realistic, functional results with unprecedented precision. As industries continue to adopt this technology, the future of design and production looks more versatile than ever.
PolyJet technology is revolutionizing the world of 3D printing with its ability to combine multiple material properties into a single part. To explore more about different 3D printing technologies, check out our comprehensive overview of 3D printing technologies.





[…] Learn how PolyJet technology enables the creation of parts with multiple properties in a single prin… […]