Table of Contents
Introduction to 3D Printing in Custom Drone Component
The advent of 3D printing has revolutionized various industries, and drone manufacturing is no exception. Traditionally, drone components were designed and produced using conventional methods, which often led to high costs, long production times, and limited design flexibility. However, 3D printing offers drone manufacturers a powerful tool for creating custom components quickly and affordably. Customization in drone design is becoming increasingly important to meet specific needs, such as payload requirements, flight characteristics, and operational environments. This article explores how 3D printing is transforming the design and manufacturing of drone components.
Also Read: How to Design 3D Printed Drone Parts for Enhanced Performance
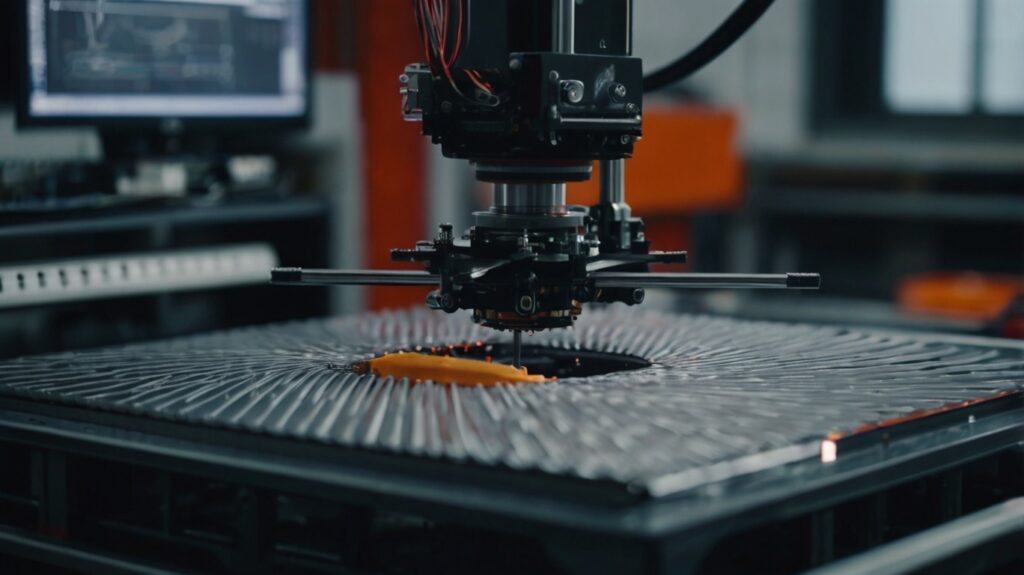

Benefits of 3D Printed Drone Parts
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, offers numerous advantages when it comes to producing drone parts. The technology has revolutionized the drone industry by providing innovative solutions that enhance the functionality, performance, and efficiency of drones. The following are some of the key benefits of using 3D-printed parts in drone design and manufacturing:
Customization and Design Freedom
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing in drone manufacturing is the freedom it provides for customization. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which are often limited by the constraints of molds, tools, and machine capabilities, 3D printing enables drone manufacturers to design and produce parts that perfectly meet the unique needs of a specific application.
For example, 3D printing allows for the creation of parts with intricate geometries that provide structural support while minimizing weight. Designers can experiment with various shapes and structures, optimizing each component for its specific function. Whether it’s a lightweight frame designed for racing drones or a custom mount for high-resolution cameras in inspection drones, 3D printing allows for a level of design freedom that was previously impossible.
This customization extends beyond just the parts themselves. Manufacturers can easily adapt designs to meet different customer requirements, experiment with new innovations, or make rapid improvements to existing models, all without the need for expensive tooling or molds. This opens up possibilities for producing small runs of highly specialized components without incurring prohibitive costs.
Material Versatility
Another major benefit of 3D printing is the ability to use a wide range of materials for different drone parts. Traditional manufacturing methods may be limited to certain materials or require extensive retooling to work with new substances, but 3D printing allows manufacturers to select from an ever-growing list of materials, each with specific characteristics suited to different needs.
Some common materials used for 3D printing drone parts include:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): Often used for lightweight parts and prototyping, PLA is biodegradable and easy to work with, making it ideal for initial designs or non-load-bearing components.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Known for its durability, heat resistance, and impact strength, ABS is commonly used for drone frames, propellers, and housings.
- Nylon: Nylon offers excellent durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear and tear, making it a preferred choice for drone parts that experience constant movement, such as gears and landing gear.
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced Filament: For high-performance parts, carbon fiber-reinforced materials offer an excellent balance of strength and lightness, often used in racing drone frames and propellers.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): TPU is a flexible and durable material often used in parts such as propellers and rubberized components, offering shock absorption and wear resistance.
The ability to select the ideal material for each component based on the demands of the specific application ensures drones are optimized for performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Cost Efficiency
Cost is one of the most compelling reasons for incorporating 3D printing into drone manufacturing. Traditional manufacturing methods often require significant upfront investment in molds, tooling, and machines. Additionally, creating custom parts or prototypes can be expensive and time-consuming.
With 3D printing, the cost of producing a part is dramatically reduced. There’s no need for complex molds or custom tooling, and parts can be printed on demand, cutting down on storage costs and reducing waste. This makes 3D printing particularly beneficial for low-volume production runs and prototype testing. Manufacturers can quickly iterate on designs, test different configurations, and make modifications without incurring additional costs associated with traditional manufacturing.
The ability to produce custom parts without the overhead of traditional processes also reduces the cost of repairs and replacements. Drone parts, such as frames or motors, are often damaged or worn out during use. With 3D printing, these parts can be replaced quickly and inexpensively, improving the longevity and overall cost-effectiveness of drone systems.
Faster Prototyping and Development
The speed at which prototypes can be produced is one of the most significant advantages of 3D printing. Traditional prototyping methods, such as injection molding or CNC machining, can take days or even weeks to create a new part, especially when modifications are needed. With 3D printing, however, prototypes can be produced in just hours, allowing designers to test and iterate quickly.
This rapid prototyping capability speeds up the product development cycle, allowing companies to bring new drone designs to market faster. It also fosters innovation, as designers can experiment with new ideas, materials, and configurations without worrying about the lengthy and costly delays associated with traditional manufacturing methods. As a result, drone manufacturers can respond to market demands, customer feedback, and new technological advancements much more efficiently.
Lightweight Components for Enhanced Performance
One of the primary goals in drone design is to reduce weight without sacrificing strength or functionality. Lighter drones are more fuel-efficient, have longer battery life, and can carry more payload. 3D printing plays a crucial role in achieving this by allowing for the production of lightweight parts that are still strong and durable.
Through the use of advanced materials such as carbon fiber and flexible filaments, 3D printing makes it possible to create parts that are both lighter and stronger than traditionally manufactured components. The ability to precisely control the material deposition process means that parts can be optimized to use minimal material while maintaining structural integrity. For example, custom frames and propellers can be designed with internal lattice structures that reduce weight while preserving strength.
This lightweight advantage is particularly valuable in applications like drone racing or long-endurance flights, where reducing weight can improve speed, flight time, and overall performance.
On-Demand Production and Supply Chain Flexibility
3D printing offers significant benefits in terms of supply chain flexibility and the ability to produce parts on demand. Traditional manufacturing methods often require manufacturers to hold large inventories of parts, which can be costly and take up valuable storage space. Additionally, any disruptions in the supply chain can delay production.
With 3D printing, manufacturers can produce parts as needed, eliminating the need for extensive stockpiling and reducing the risks associated with supply chain disruptions. This on-demand production also allows companies to create parts locally, reducing shipping costs and lead times. For drone manufacturers, this flexibility is especially important when dealing with repairs, maintenance, or upgrades, as parts can be printed and delivered quickly without the need to wait for third-party suppliers.
Furthermore, 3D printing enables manufacturers to maintain a continuous flow of new and improved parts, keeping pace with technological advancements and customer demands without the traditional barriers of mass production.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction
3D printing is a more sustainable manufacturing process compared to traditional methods. Conventional manufacturing techniques, such as injection molding or machining, often result in significant material waste, as excess material is cut away or discarded during production. In contrast, 3D printing is an additive process, meaning material is deposited layer by layer, reducing waste to a minimum.
Additionally, many 3D printing materials are recyclable, and manufacturers can reuse failed prints or scrap material, further contributing to sustainability efforts. The ability to print parts locally and on demand also reduces the environmental impact of shipping and transportation.
For drone manufacturers and operators, the reduced waste and the possibility of using eco-friendly materials make 3D printing an attractive option from both an environmental and economic standpoint.
Applications of 3D Printed Parts in Drones
3D printing has unlocked numerous possibilities for customizing drone components, leading to a wide range of applications across various industries. From agriculture to emergency services, drones equipped with 3D-printed parts offer greater efficiency, versatility, and performance in their respective tasks. Below are some of the key applications of 3D-printed parts in drones:
Inspection Drones
Inspection drones are widely used in industries like construction, energy, utilities, and telecommunications for tasks such as infrastructure inspection, powerline monitoring, and bridge analysis. 3D printing plays a significant role in the customization of inspection drones by enabling the creation of lightweight, durable frames and specialized components that can carry heavy payloads, such as cameras, thermal sensors, or LiDAR systems.
Custom Components:
- Camera mounts: These mounts hold cameras and sensors in the ideal orientation for capturing high-resolution images or video during inspections.
- Sensor housings: Protect sensitive equipment from environmental factors like dust, moisture, and vibration.
- Frames and supports: Tailored to specific payloads and operational environments, ensuring that drones are stable during flight and capable of handling the weight of complex inspection equipment.
3D printing allows these parts to be designed and produced quickly, reducing downtime and costs during maintenance and part replacement.
Agricultural Drones

Agricultural drones are transforming farming practices by offering advanced solutions for crop monitoring, precision spraying, and soil analysis. These drones rely heavily on 3D-printed parts to ensure they are tailored to the unique needs of agriculture, such as the ability to carry specialized payloads or withstand environmental stresses like dust, moisture, and fluctuating temperatures.
Custom Components:
- Sprayer systems: 3D-printed nozzles, reservoirs, and distribution systems help ensure precise spraying of fertilizers and pesticides, reducing waste and improving crop yields.
- Frames: Lightweight yet robust frames that provide stability while carrying heavy payloads like cameras, multispectral sensors, or nutrient dispensers.
- Sensor mounts: Designed for specialized environmental sensors, these mounts help collect data related to soil health, crop conditions, and pest activity.
3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and customization of these drone parts, ensuring the drones are optimized for a variety of farming applications.
Racing Drones

In drone racing, speed and agility are critical, and 3D printing plays a vital role in giving pilots the competitive edge. Racing drones require lightweight, aerodynamic, and durable parts to withstand high-speed collisions and rapid maneuvers. 3D printing enables designers to experiment with new frame designs, propeller shapes, and other components to improve the drone’s performance.
Custom Components:
- Frames: Lightweight yet strong frames are essential for racing drones. 3D printing allows for the creation of custom frame designs that are tailored for optimal aerodynamics and crash resistance.
- Propellers: Custom propellers can be designed for greater thrust, efficiency, and stability during high-speed flights. Materials like nylon and TPU are commonly used for their durability and flexibility.
- Motor mounts: Customized mounts that provide optimal alignment and support for motors to enhance control and maneuverability.
The ability to quickly modify designs and print new parts means that racing drone enthusiasts can optimize their drones for peak performance, giving them an edge in competitive events.
Search and Rescue Drones

Search and rescue (SAR) drones are increasingly being used in emergency situations, such as natural disasters or accidents, to locate and assist people in difficult-to-reach areas. These drones often need to operate in harsh environments, such as extreme weather conditions or dense forests. 3D printing allows for the creation of rugged, reliable components that are customized to perform specific SAR tasks, such as carrying rescue payloads, thermal cameras, or GPS systems.
Custom Components:
- Frames: Sturdy frames are essential for SAR drones, as they need to endure extreme conditions and carry heavy equipment like thermal imaging cameras, infrared sensors, or life-saving devices such as defibrillators or first aid kits.
- Payload attachments: These attachments can carry specialized equipment, such as ropes or baskets, for delivering supplies or rescuing stranded individuals.
- Camera and sensor mounts: These mounts are specifically designed to securely hold SAR sensors, including infrared cameras, heat sensors, and GPS devices, ensuring that the drone can locate people or assess dangerous environments from the air.
3D printing allows SAR drones to be equipped with customized components that ensure high performance during rescue missions, providing more effective and timely assistance to those in need.
Environmental Monitoring Drones

Environmental monitoring drones are used for a wide variety of tasks, including air quality measurement, wildlife tracking, pollution detection, and environmental conservation. These drones often operate in remote or harsh environments, where rugged components are necessary to ensure reliable performance. 3D printing helps in the creation of custom parts that are lightweight yet durable enough to withstand exposure to the elements.
Custom Components:
- Sensor housings: These housings protect delicate environmental sensors, such as air quality meters, from environmental factors like wind, rain, or extreme temperatures. The housings are often designed with specific features like heat dissipation vents or water-tight seals to ensure that sensors remain functional in all conditions.
- Frames: Custom frames for environmental monitoring drones allow designers to build drones that are lightweight enough to carry environmental sensors without sacrificing durability or flight stability.
- Propeller blades: 3D-printed blades can be tailored to provide the optimal lift for drones carrying sensitive payloads over long distances, such as for pollution detection or wildlife monitoring.
By enabling the production of parts that meet specific requirements, 3D printing enhances the efficiency and versatility of environmental monitoring drones, making them more effective tools for conservation efforts and environmental research.
Military and Surveillance Drones

Military and surveillance drones require specialized designs to meet the demanding needs of defense applications, including surveillance, reconnaissance, and tactical operations. These drones often operate in hostile environments, requiring parts that are not only highly durable but also customized to fit specific mission requirements. 3D printing allows for the creation of advanced components that support these missions.
Custom Components:
- Stealth coatings and structures: 3D printing enables the production of complex components that can be integrated with stealth technologies, allowing drones to remain undetected during surveillance missions.
- Payload compartments: Custom compartments can be created to house sensitive surveillance equipment, ensuring the security and functionality of the equipment during flight.
- Camera mounts and enclosures: Specialized mounts that hold high-definition cameras or surveillance gear can be 3D printed to suit the specific needs of military or surveillance operations.
For defense and surveillance applications, the ability to customize every aspect of the drone’s design makes 3D printing an invaluable tool for ensuring mission success.
Key Components Commonly 3D Printed
Several drone components are ideal candidates for 3D printing, offering benefits in terms of weight reduction, customization, and ease of production.
| Component | Function | Materials Used |
|---|---|---|
| Frames | Provide the structural support for the drone’s components | Carbon fiber, ABS, PLA |
| Propellers | Generate thrust for flight | Nylon, TPU, PETG |
| Camera Mounts | Secure cameras and sensors in place | ABS, PLA, PETG |
| Landing Gear | Provide shock absorption during takeoff and landing | ABS, TPU, Nylon |
| Sensor Housings | Protect sensitive sensors and electronics from the environment | PLA, ABS, Nylon, PETG |
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing in Drone Manufacturing
Despite its many advantages, 3D printing in drone manufacturing does come with certain challenges and limitations.
Material Restrictions
While 3D printing offers a wide variety of materials, the strength and performance of 3D-printed parts can sometimes fall short compared to traditionally manufactured components. The mechanical properties of some 3D-printed materials may not be suitable for high-stress applications, such as those involving heavy payloads or high-speed flight.
Strength and Durability Concerns
Although 3D printing allows for the creation of complex shapes, the resulting parts may not always match the strength and durability of traditionally produced components. For example, parts like propellers or landing gear might wear out more quickly if not made from the appropriate material or design. Engineers must carefully select materials and optimize designs to ensure that parts can withstand the forces they will encounter during flight.
Limited Scalability for Large-Scale Production
While 3D printing is excellent for rapid prototyping and small-scale production, it may not be cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing. The time required to print individual parts and the limitations of current 3D printing technology can make it less suitable for mass production of certain drone components.
Conclusion
3D printing plays a crucial role in the customization and innovation of drone component design. It allows manufacturers to create lightweight, durable, and specialized parts that enhance drone performance across a wide range of applications, from inspection to environmental monitoring. However, challenges such as material limitations and scalability must be addressed for 3D printing to realize its full potential in large-scale drone manufacturing. As technology advances, the role of 3D printing in the drone industry is expected to grow, bringing new possibilities for innovation and efficiency.




[…] Also Read: The Role of 3D Printing in Custom Drone Component Design […]